Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) and Smart Systems
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and smart systems are two interrelated concepts that have been driving important advancements in multiple industries. The fundamental idea supporting IIoT is that smart machines are not only well than humans at taking and studying data in real-time, but they're also finer at communicating significant details that can be utilized to make business decisions quicker and more precisely.
What is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
The Industrial Internet of Things refers to the combination of physical industrial devices and machines with sensors, software, and network connectivity, allowing them to collect, exchange, and analyse information. This network of a connected device enables machines to communicate with each other and with centralized systems to enhance automation, data analytics, and decision-making processes in industrial settings. The key components of IIoT are Sensors and Actuators, Connectivity, Cloud Computing, Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence and Security. IIoT applications span various industries, including manufacturing, transportation, energy, healthcare, agriculture, and so on. Some examples include predictive maintenance in manufacturing, smart grid optimization in energy, and remote monitoring in healthcare.
Difference between IIoT and IOT
| IIOT |
IOT |
| IIOT is called the employing of the internet of things for industrial applications and fields. |
It is described as the physical devices that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to send out the data and to communicate between the devices via the Internet. |
| Examples: Amazon warehouse, smart robotics, Air bus etc. |
Examples: Sensors, Smartwatches, Mobile Phones, ACs etc. |
| IIoT transacts with wide-ranging networks |
IoT transacts with small-time network |
| Provides remote on-site programming |
Provides simple off-site programming |
| It needs strong security to safeguard the data |
IoT needs identity and privacy |
| Prolonged lifecycle |
Brief product lifespan |
| Highly dependable |
Less dependable |
What are Smart Systems?
A smart system is an integrated set of connected components that use improved technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, to make advanced decisions and minimize operations. These systems aim to enhance efficiency, convenience, and overall performance by using data-driven insights to respond dynamically to varied conditions. The key characteristics of smart systems are Data-Driven, Automation, Learning Capabilities, Connectivity and Energy Efficiency.
Some examples of smart systems include Smart Home, Smart Cities, and Intelligent Transportation Systems. The convergence of IIoT and smart systems is evident in applications like Industry 4.0, where intelligent factories leverage IIoT technologies to create highly automated, data-driven production environments, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. The integration of these two concepts is transforming industries by providing new opportunities for optimization and innovation.
Industrial Internet of Things and Smart Systems:
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) and smart systems are two closely related concepts that are driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution. IIoT refers to the use of sensors and actuators to collect and analyze data from industrial equipment and processes. This information can then be used to enhance efficiency, productivity, and safety. Smart systems are self-aware and self-managing systems that use IIoT data to take decisions and actions without human intervention.
Why it is beneficial?
There are many benefits in using IIoT and smart systems in manufacturing and other industrial settings.
- Improved efficiency: IIoT and smart systems can help to identify and eliminate inefficiencies in manufacturing processes. This can result in essential reductions in waste, energy consumption, and production costs.
- Increased productivity: IIoT and smart systems can help to enhance the productivity of manufacturing workers. This is done by providing workers with real-time data about the status of equipment and processes, as well as by automating tasks that are currently done manually.
- Enhanced safety: IIoT and smart systems can help to improve security in manufacturing settings. This is done by monitoring equipment and processes for potential hazards, and by alerting workers to potential risks.
Improved decision-making: IIoT and smart systems can help to improve decision-making in manufacturing settings. This is done by providing decision-makers with real-time data and insights, which can help them to make advanced decisions about production, scheduling, and maintenance.
What are its applications?
Here are some examples of how IIoT and smart systems are being used in manufacturing today:
- Predictive maintenance: IIoT sensors can be used to monitor the condition of equipment and predict when maintenance is needed. This can help to prevent unplanned downtime and improve the reliability of equipment.
- Remote monitoring: IIoT sensors can be used to monitor equipment and processes remotely. This allows manufacturers to track the status of their operations from anywhere in the world.
- Automated quality control: IIoT sensors can be used to automate quality control checks. This can help to ensure that products are consistently meeting quality standards.
- Optimized production scheduling: IIoT data can be used to optimize production scheduling. This can aid mitigating wastage and increase productivity.
- Futurisic Farming: By implementing connected IIoT projects in large farms, the farmers can keep a track of the yield from the field to the market. In huge farms, physical surveying is susceptible to a lot of inaccuracies. Farmers can analyse several agricultural attributes employing satellite imaging and IIoT
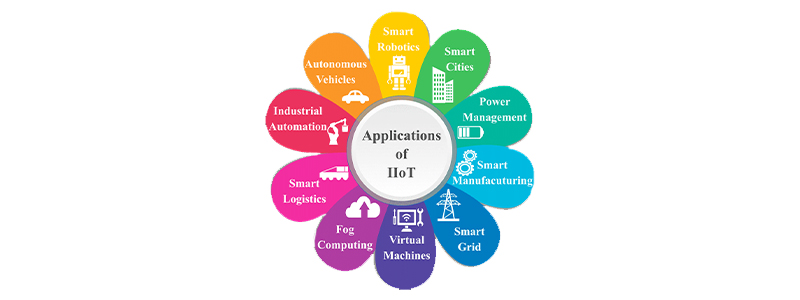
These are just a few examples of the many ways that IIoT and smart systems are being used in manufacturing today. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications for these technologies in the years to come.
What are the risks and challenges of IIoT?
The major risks associated with IIoT use pertain to safety. It's relatively general for IIoT devices to continue using default passwords, even after they have been placed into production. Similarly, many IIoT devices transfer information as clear text. These conditions would make it relatively easy for an attacker to intercept the information coming from an IIoT device. Similarly, an attacker could take over an insecure IIoT device and use it as a base for launching an attack against other network sources.
Security is a big problem for those who are in-charge of an organization's IIoT devices. As an organization adopts many IIoT devices, it will become increasingly essential to adopt an effective device management strategy. More particularly, companies must be able to precisely discover IIoT devices that shield the use of unauthorized devices. Establishing a means of identifying each individual device is also crucial for tasks such as replacing a false device or performing a device refresh. Patch management poses additional substantial encounter with regard to IIoT devices. It's becoming increasingly general for device manufacturers to issue periodic firmware updates. Companies should have a competent method of checking devices to see if they have the contemporary firmware installed and deploying new firmware if required. Moreover, such tools should stick to the concern's established maintenance plan in order to avoid disruption of operations.
Conclusion:
The assessment and decision making that go into the advancement and deployment of an IIoT implementation can be formidable. It can support your queries to identify the correct result for your requirements at any point along the way, from starting project aiming to complete engineering and services.
Whether you want to signify the ROI of a fresh product or requirement to meet a strict deadline for compliance or market pressures, it can partner with you to achieve those goals. Time to market can be importantly critical when there is a short-lived window of chances to get ahead of contention.
Working with a company that has proven professional consulting and engineering keep up not only gives you the assurance that you can meet deadlines and launch dates, but also assist you complete design reviews and get certification assistance when your resources stretched thin.
About the Author
Ms. S. Seema is an Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science (UG & PG), Dwaraka Doss Goverdhan Doss Vaishnav College, Chennai and has experience in teaching for more than a decade. I am keen to learn new technologies especially AI and Machine Learning. I am having experience on various committees related to Institutional enrichment.