The Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance (eGRC) market has evolved exponentially since its inception ten years ago. According to Gartners Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) Magic Quadrant, the key differentiator is the delivery of advanced risk management functionality by establishing a good governance and management. Todays market need is risk and regulatory compliance, combined with analytics to offer solution at an enterprise level. Every industry, due to the growing business demands in security, data privacy, external reporting obligations, stakeholder transparency stringent regulatory norms, are foreseeing unprecedented requirement for Governance, Risk and Compliance management at an enterprise level.
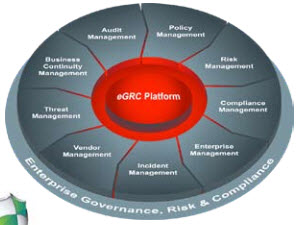
Enterprise GRC frameworks appraise the strategic risks and objectives throughout the business, connect objectives with enterprise risks, augment decision making process and reduce loss. GRC has moved from more than just processes and tools, which span the enterprise, to essential philosophy required to be high on transparency and integrity.
Regulatory requirements continue to grow, making enterprise GRC more and more challenging. The present trend is that the faculty of GRC is to provide enterprise-wide risk assessments and hauling evidence from organizational silos. Legal and regulatory compliance is a key part of the effective governance of an enterprise while assessing risks. All enterprise activities include control activities that are designed to ensure compliance not only with externally imposed legislative or regulatory requirements but also with enterprise governance resolute of principles, policies, process and procedures. Exercising governance and management effectively in practice requires using all enablers appropriately.
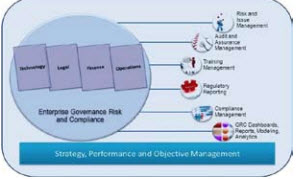
A GRC program can be established in an organization to focus on any individual area within the enterprise, or bring in a fully integrated mode which can help to work across all areas of the enterprise, using a single framework by linking strategic risks with other governance, risk, and compliance business processes, Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance (eGRC) for risk management provides structure, visibility, and transparency to your risk management program. Let us now look into some of the key inter related components that constitute the Governance, Risk and Compliance program.
Enterprise Governance
The Enterprise Governance is defined as "the set of responsibilities and practices exercised by the board and executive management with the goal of providing strategic direction, ensuring that objectives are achieved, ascertaining that risks are managed appropriately and verifying that the organizations resources are used responsibly" (Information Systems Audit and Control Foundation, 2001). An effective governance framework warrants commitment from the senior management, Strategic Alignment, Maturity Assessments, Value Delivery and Management, Resource Management, Performance Management and Service Management. The IT capability is threaded into the long term consequences of decisions made by senior management in an organization. An enterprise consists of multiple domains, systems, resources, capabilities, each striving to meet the organization business goals which are governed by different regulatory affairs and contractual obligations.
The governance body of an enterprise should have the ability to respond rapidly to the market needs, inter-operate seamlessly, well equipped in managing enterprise, Risk Management, Disaster Planning, scale in magnitude and be responsive to internal and external changes. The Governance framework and structure should be defined such that there is a control in every aspect of the business in the organization, regulate performance and comply with the regulatory needs. Enterprise Governance also warrants that organization goals objectives are realized by evaluating and understanding stakeholder requirements, set direction through prioritization and decision making, continuous monitoring and improvement and align to the market needs. The framework encompassing the above said aspects will establish systemic governance and directed management through interconnected enablers in the system.
Risk Management at Enterprise level
The present outlook of Risk Management is based on the compelling business demands and ever changing market needs which gives us a different perspective that risks are not hazards to be avoided altogether, but can also be an opportunity to be embraced to do business better. This also helps in efficient use of resources, promotes continual improvements and increased certainty in all aspects of business.

Risk Management can also be performed at an enterprise level through interconnected enablers in the system. The Risk Assessment done at enterprise level will be a High Level Risk Assessment and Management (HLRA).The Enterprise Risk Management is an ongoing process and is an integral part of how an organization operates. The Risk Management Framework needs to be a holistic, future based, process oriented approach for Risk Management for creating true business value. This system measures risk using a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods to set a standard method for analyzing risk across many functions within the enterprise. Moving from traditional risk mitigation and planning towards risk tolerance to have more business value. Enterprise Risk Management also stresses the management of operational and strategic risks.
Compared to the traditional risk management methods, Enterprise Risk Management facilitates to anticipate problems before they become a threat to business. The mandatory requirements for effective risk management at an enterprise level are Senior Management and Stakeholder Commitment, Risk Management Policies, Process and procedures well established for the most prominent risks with specific objectives and parameters, distinctly defined responsibilities for managing and controlling risk, ongoing awareness training, tracking, testing and monitoring of all programs, process and procedures, reports and score cards including audits. Last but not the least, regardless of what the risk appetite may be, every risk should be assessed and kept under control.
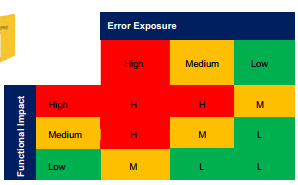
Business and Regulatory Impact Assessments to address Enterprise Risks
A Business and Regulatory Impact Analysis (BRIA) predicts the after effects of disruption of a business function and process in an uneventful case of disaster. This assessment process musters information needed to develop recovery strategies in case of an occurrence of an event. The business impact assessment warrants that the potential loss scenarios be identified during a risk assessment. BRIA is an essential component of an organization business continuance plan; it includes an exploratory element to expose any vulnerability case of a disastrous event, and a planning component to develop strategies for minimizing risk and impact. The result of this analysis is a BRIA report, which describes the potential risks specific to the enterprise, program or a project that is getting evaluated for. Loss of income, Regulatory fines, Contractual realities and obligations, Business SLA are some of the vital business components which will be assessed.
The BRIA process can be done at an enterprise level, project level and for services too. The BRIA done at enterprise level will be a High Level BRIA (HLBRIA). The Service BRIA starts in the operational state of a service in service oriented architecture. Business resilience plan to safe guard critical business processes can be derived out of the business impact assessment.
Read More
Business Continuity Management (BCM)
A BCM programmed at enterprise level aims at providing integrated responses to multiple risks. The BCM programs typically emphasize on the continuous assessment of business needs, acceptable levels of risk and responding with a set of defined processes and exact infrastructure designed to augment operational availability. The recovery strategies will be formulated based on the corresponding recovery objectives and the outcome of the BRIA. An effective response demands meticulous planning, regular rehearsal /testing and awareness across organization.
Enterprise Training
Enterprise training comprises of awareness training and training of individuals who will be a part of the Enterprise Governance and risk management team. The core members of the team will have to be conversant on the design and implementation of appropriate enterprise governance and risk management system which encompasses the policies, procedures, practices, and accountability required to establish the right levels of risk management in compliance with current standards and other requirements for the enterprise. The training should also be focused on creating awareness - Training, Development and Education with every member of the organization on the Enterprise Risk Management Plan. Training is also mandatory on the awareness on the regulatory compliance for the enterprise.
The Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance framework
The eGRC framework and solutions integrated with the core business as an enterprise will also help to bridge between audit, risk and compliance groups, increasing business value while decreasing operating costs and minimal risk loss. Enterprise Modeling (EM) is a method which can be used to create a logical model or a framework for an organization. Complex organizations with well-established standards provide form and inter- operability to Enterprise Modeling practices.
A Framework that can be referenced for Governance and Risk is COBIT 5. This framework helps enterprises to create optimal value from IT by maintaining a balance between realizing benefits and optimizing risk levels and resource use. The COBIT 5 framework uses a core set of control material, charted to the primary governance factors in the system. The set-up of governance framework and maintenance in line with the recommendations from COBIT will help to, ensure benefits delivery, ensure risk optimization, warrant resource optimization and ensure stakeholder transparency.
One other aspect to progress successfully using eGRC frameworks is the Data Integrity, Analytics and Metrics. The exactness and integrity of GRC information is a mandate now and the corporates are looking for reassurances that the organization is making all-encompassing risk management rulings based on reliable information which is more archetypical. There is an immense need for reliable analytics to assist and identify the relationship of risks from various departments of the organization and to determine which risks are priorities at the enterprise level. This will help to build a consistent heat map across the entire organization. Analytics and genuine information will help to arrive on an accurate decision at organization level. This will support the businesses to cruise with the minimum loss in case of unavoidable risks that may occur. Business intelligence and data governance will factor more prominently in GRC decisions.
Organizations are now increasingly planning GRC roadmaps with cross-silo integration between departments. IT GRC is a better choice to start as a quick win in most of these implementations. It is definite, and it can be used to construct an extensible framework for all other GRC programs in future for other departments in an enterprise. Also, the GRC market today is more akin to the breadth of the IT security market. Another interesting finding is that the Mobile, Social, and Cloud Technologies will begin showing practical value for GRC. The access to huge data will help the businesses to draw in the required information and judgments to run business smoothly.
To conclude, Enterprise GRC frameworks will enable standardization, automation and help manage key aspects of every process at organization level. Risk and Compliance integrated with information and analytics will offer more precise judgments which will help businesses to surge more successfully in the scenario of ever changing regulatory and compliance needs. The Governance, Risk and Compliance Metrics will be perceived as key indicators of business performance. The vendors who address the vast and diverse GRC Needs with capabilities such as workflow flexibility, user interface flexibility, data model, extensibility, and ability to support new and changing market requirements (Ref: Forrester wave) have a substantial market landscape to source on.
Acronym & Abbreviations:
• BCM - Business Continuity Management
• BCP - Business Continuity Planning
• BRIA - Business and Regulatory Impact Assessments
• COBIT - Control Objectives for Information and
• Related Technology eGRC - Enterprise Governance,
• Risk and Compliance
• GRC - Governance, Risk and Compliance
• HLBRIA - High Level Business Regulatory an Impact Assessments
• HLRA - High Level Risk Assessment and Management
• IT - Information Technology
About the Author
Radhika brings in around Fifteen plus years of experience to her role as a Principal consultant a with expertise in Healthcare & Life Sciences domain . Her experience focuses Strategic Digital Transformation Solutions & Research based Consulting ,Lifesciences GRC, Global Delivery Management, Governance, Strategy & Transition Management and M&A Compliance.